Who is a defectologist and how can he help a child with mental retardation?
In a broad sense, a defectologist is a specialist who studies, trains, educates and socializes children with developmental disabilities.
What functions does a defectologist perform in kindergarten?
Firstly , a defectologist in a kindergarten conducts a complete and detailed examination of each child for the characteristics of his cognitive and social development, during which he determines the child’s ability to learn and play, which helps him organize work with this child in such a way as to maximally correct the identified developmental deficiencies .
Secondly , a defectologist increases the cognitive activity of children and at the same time develops basic mental processes such as thinking, imagination, attention, curiosity, memory, perception.
Third , the work of a defectologist is aimed at the formation and development of children’s play activities, which is the main activity for children of this age.
Thus, the goal of the correctional pedagogical work of a defectologist with a child with mental retardation in a preschool institution is formation of a psychological basis for the full development of his personality.
To the teacher-defectologist it is important to form cognitive processes, which are the basis for the development of thinking: memory, attention, various types of perception, visual, auditory, motor functions and intersensory connections, cognitive and creative activity of the child. In addition, the work creates conditions for the formation of leading activities. When these goals are achieved, full preparation for studying in a public school is possible.
A speech pathologist teacher works closely with doctors, educators, a psychologist, music director, physical education instructor and parents.
A speech pathologist teacher conducts subgroup and individual lessons in the group.
Subgroup classes are conducted in the following disciplines:
- familiarization with the outside world (all age categories);
- development of elementary mathematical concepts (all age categories).Getting to know the world around you
The main goal of the classes is to broaden the horizons of children, clarify their ideas about objects and phenomena, nature, and social reality; children get acquainted with the basics of life safety and environmental knowledge. During classes, the tasks of speech development are necessarily solved, mainly enriching the vocabulary and clarifying the meanings of words. The structure of classes includes games and exercises aimed at developing cognitive processes.Development of elementary mathematical concepts
Mathematical development is a powerful tool:
- for sensory development (orientation in color, shape, size of objects, grouping sets of objects according to given characteristics, etc.);
- for cognitive development (the ability to analyze, classify, compare and generalize, establish cause-and-effect dependencies and patterns, etc.);
- speech development (formation of skills in constructing detailed statements, logical and grammatical structures);
- preparation for schooling.In individual lessons, the speech pathologist teacher:
- develops the basic types of memory and attention, perception and thinking, imagination;
- stimulates the development of cognitive activity, the formation of educational motivation;
- improves motor functions: general and fine motor skills, forms elementary graphomotor skills;
- consolidates basic concepts learned in subgroup lessons that the child has not mastered sufficiently;
- reinforces basic concepts on previously studied topics.In addition to classes with the child, the speech pathologist provides consultations to parents, during which parents learn the necessary techniques for teaching their child.
However, parents need to remember that the child spends most of his time not in kindergarten, but in the family. Therefore, the speech pathologist’s sessions with the child alone will not give the same result that can be obtained with long-term and focused work of a specialist. together with parents.
A defectologist can do a lot for a child, but he cannot replace his parents in everyday life!
Mental retardation (mental retardation) is an unpleasant diagnosis, but not fatal. If you know how to properly conduct exercises and games with such children, you can achieve great results. You just need to know which games are best suited for a child with mental retardation, which methods and activities are more beneficial. Let's consider this issue in more detail.
Corrective classes for children with mental retardation
Correctional classes for children with mental retardation are designed taking into account the complex problems that arise in the emotional state of the child.
The purpose of correction techniques
The goal of correctional techniques for children with mental retardation is the development of:
- mental functions;
- motor sphere;
- adaptation to the conditions surrounding the child.
Corrective techniques are aimed at developing memory, imagination, and attention.
Correctional classes help the child navigate space and time, sensory functions develop, motor skills develop, the child learns to play, be friendly, and sociable.
How are correctional classes conducted?
Most often, correctional classes are held in groups of 10 people once a week for 15-30 minutes. Classes provide mental security for the baby. Communication with the teacher occurs strictly according to the emotional needs of the child (from 15-30 minutes depending on the age group). All exercises for children with mental retardation are united under one theme and plots, which include favorite or simply well-known characters from fairy tales, cartoons, and often the main characters can be animals. At the same time, all the heroes find themselves in certain life situations, traveling through fairy-tale lands with children. During such games, children concentrate their attention, develop memory and logical thinking. At the time of conducting correctional games and exercises for children with mental retardation, teachers (speech pathologist, teacher, music director) act as one whole, creating an illusory and colorful, fairy-tale world for the children.
For good results during correctional classes, ensure a uniform alternation of mental and physical stress:
- warming up and doing exercises to improve muscle tone;
- classes to develop attention, memory, and thinking;
- the sense of tempo and rhythm is developing;
- exercises for coordinated interaction of speech and movements;
- voice and breathing develop;
- facial expressions and competent speech develop;
- The baby's creative abilities develop.
Corrective classes with musical accompaniment
Most often, games with musical accompaniment are used for activities with children with developmental delays. Music has a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state of a child, allows him to perform certain actions to the beat of music, or it is often used to understand the time period during which certain actions must be performed. Games and exercises during correctional classes develop in a child:
- development of oral speech;
- rich vocabulary;
- ensure back alignment;
- help the child navigate in space and time.
Moscow Humanitarian Institute named after. E.R. Dashkova
Faculty of Humanities
ABOUT psychology department
SUBJECT: SPECIAL PSYCHOLOGY
CORRECTIONAL CLASSES
FOR CHILDREN WITH SPECIAL DISTRIBUTION
Completed by a student
3 courses of correspondence (accelerated) department
Polukhanova A.A.
Teacher:
Buchatskaya M.V.
Moscow
2011
Introduction
Corrective classes for children with mental retardation
Conclusion
INTRODUCTION
(ZPR) MENTAL DEVELOPMENT RETARDATION is a violation of the normal pace of mental development. It manifests itself in a slow pace of maturation of the emotional-volitional sphere, which manifests itself in the inability to concentrate on the task at hand, in intellectual deficiency (mental abilities do not correspond to age).
REASONS FOR THE APPEARANCE OF DPR. The main reason is mild organic brain damage, which can be congenital or occurred during the birth or early period of a child’s life; there can be unfavorable pregnancy, birth pathology, social factors: pedagogical neglect, limited emotional contacts with the child in the early stages of development, bilingualism.
ZPR is not inherited, but in some cases there is a genetic cause of central nervous system failure.
THERE ARE TWO OPTIONS OF ZPR: medical and pedagogical.
MEDICAL
Based on neurological analysis in young children, it was proposed to distinguish 2 types of mental retardation based on underdevelopment.
· Benign or non-specific. It is not associated with brain damage and is compensated with age under favorable environmental conditions, even without specific measures. Manifests itself in delayed motor functions.
· Specific or cerebral-organic developmental delay associated with damage to brain structures and partial retardation of their functions.
PEDAGOGICAL
· Constitutional origin– the state of delay is determined by the heredity of the family constitution. In its slow pace of development, the child seems to repeat the life scenario of his father and mother. Genetic predisposition manifests itself in high sensitivity to environmental development factors. By the time they enter school, these children have a discrepancy between their mental age and their passport age; in a seven-year-old child it can be correlated with children 4–5 years old. The immaturity of mental appearance manifests itself in the emotional-volitional sphere with relatively preserved cognitive activity, i.e. immaturity of the emotional-volitional sphere leads to underdevelopment of the cognitive sphere. Children with constitutional mental retardation are characterized by a favorable developmental prognosis, subject to targeted pedagogical influence, play-based activities available to the child, and positive contact with the teacher. Such children are compensated by the age of 10–12 years. Particular attention must be paid to the development of the emotional-volitional sphere.
· Somatogenic origin– long-term chronic diseases, persistent asthenia (neuropsychic weakness of brain cells) lead to mental retardation. Such children are born to healthy parents, and developmental delay is a consequence of diseases suffered in early childhood: chronic infections, allergies, etc. primary intelligence does not decrease, but due to its exhaustion it turns out to be extremely incapacitated during schoolwork. All children with this form of mental retardation have pronounced asthenic symptoms in the form of headache, increased fatigue, decreased performance, against this background, frustration, anxiety, attention decreases, memory and intellectual tension are retained for a very short time.. The emotional-volitional sphere does not differ maturity with relatively preserved intelligence. In a state of efficiency they can assimilate educational material. When performance declines, they may refuse to work. They tend to focus on their well-being and can use these abilities to avoid difficulties. Experience difficulties in adapting to a new environment. Children with somatogenic mental retardation need systematic psychological and pedagogical assistance.
· ZPR of psychogenic origin. Children in this group have normal physical development, functionally complete brain systems, and are somatically healthy. Mental retardation is caused by unfavorable upbringing conditions.
· ZPR of cerebral-organic origin. The reason for the disruption of the rate of development of intelligence and personality is severe and persistent local destruction of the maturation of brain structures (maturation of the cerebral cortex), toxicosis of a pregnant woman, viral diseases during pregnancy, influenza, hepatitis, rubella, alcoholism, drug addiction, mothers, prematurity, infection, oxygen starvation . Children in this group have the phenomenon of cerebral asthenia, which leads to increased fatigue, intolerance to discomfort, decreased performance, poor concentration, decreased memory and, as a consequence, cognitive activity is significantly reduced. A persistent lag in the development of intellectual activity is combined in this group with emotional-volitional immaturity spheres. They need systematic comprehensive help from a physician, psychologist, and speech pathologist.
CORRECTIONAL CLASSES FOR CHILDREN WITH SPECIALIST DEVELOPMENTS.
Taking into account the complex structure of emotional problems in children with mental retardation, four main phases of the process of group psychocorrection have been identified.
DYNAMICS OF GROUP PSYCHOCORRECTION OF CHILDREN WITH MENTAL DEVELOPMENT RETARDS.
| Phase | Tasks | Psychotechnical techniques | Subject of psychocorrection |
| Installation | 1. Formation of the group as a whole. 2. Formation of a positive attitude towards the lesson. 3.Diagnostics of behavior and communication patterns of children | Spontaneous games: games for nonverbal communication. Communication games | Children with mental retardation of all forms: constitutional, somatogenic, psychogenic, cerebral-organic origin |
| Preparatory | 1. Structuring the group. 2. Formation of activity and independence 3. Formation of emotional support by group members | Role-playing games. Dramatization games to relieve emotional stress | For children with mental retardation of the somatogenic form and cerebral origin with snowy social experience - dramatization games. With a psychogenic form, constitutional, without pronounced violations of social experience - role-playing games |
| Reconstructive | 1. Correction of inadequate emotional reactions to the defect. 2. Processing negative experiences. 3. Learning to independently find the necessary forms of emotional response in various situations | Acting out specific life problem situations | For children with mental retardation and severe cerebral-organic insufficiency, it is possible to involve parents |
| Fixing | 1. Consolidating adequate forms of emotional response to conflict. 2. Formation of an adequate attitude towards yourself and others | Special role-playing games suggested by children | Children with mental retardation need help from a psychologist in choosing a game. It is recommended to include parents and healthy peers or peers with milder forms of mental retardation into the game |
Based on the above-mentioned structure and stages of group dynamics, plans and schemes of psychocorrectional classes for children with mental retardation have been developed.
SCHEME OF CLASSES FOR CORRECTION OF EMOTIONAL DISORDERS IN CHILDREN WITH SPECIAL DISTRIBUTION.
| Psychotechnical techniques | Radicals for psychological observation | Criteria for the effectiveness of classes |
| Lesson 1. Purpose: introducing children to each other; formation of a positive attitude towards the lesson. | ||
| Game I. “Getting to know” balloons Children sit in a circle and take turns throwing a balloon to each other, while saying their name. After a while, you are invited to throw the ball to the person you want to play with or talk to. Game 2. “Guess who it is” A blindfolded or closed child feels other children and calls their names. Game 3. “Break into the circle” A group of children form a circle, holding hands. One of the volunteers tries to enter the circle, but the group does not let him in | The child’s attitude towards the activity Communication skills Spontaneity of behavior Emotional reactions to obstacles Preferences in choosing a partner Specific reactions (withdrawal from play, an active desire to be a leader, attitude towards failure) | Spontaneous, natural behavior of the child Manifestation of activity at the stage of classes Positive emotional background during classes |
| Lesson 2. Goal: group unity, relieving tension and constraint | ||
| Greeting Warm-up: children remember each other's names while playing with the ball. Game 1. “Who will shout louder?” Children are asked to make loud sounds. But the cry should gradually turn into a common melody (chorus). Game 2. Creating a collective drawing The psychologist invites the children to go to the board on which a large Whatman paper is attached, and with felt-tip pens draw what everyone wants, but do it in such a way that they get a common drawing. After completing the task, the drawing is collectively reviewed and discussed. | The child’s involvement in the learning process. The naturalness of children’s behavior. In the process of performing collective exercises, it is necessary to monitor what position each participant in the correction has: is not subject to group influence; quickly obeys; strives for leadership positions. | Manifestation of expressed interest in the lesson. Willing inclusion in the process of classes. Positive emotional background. During the conversation with the parents, find out how the child responded to the lesson. |
| Lesson 3. Formation of emotional support for group members by creating conditions for choice and making collective decisions. Formation of initiative. | ||
| Greeting Game I. Children's choice. The psychologist invites the children to choose a game from those that were in previous classes and make a collective decision. Game 2. “Broken Phone” The psychologist chooses a presenter who says the first word and “starts the broken phone.” Game 3. “Solve the problem” The presenter offers the children problems from the Raven matrices and Eysenck tests. Children collectively find the correct answer. Game 4. Children come up with a problem themselves and offer it to the group. | Group cohesion in solving collective problems Level of independence and activity of each child Leadership positions of group members Children with problems of group interaction need emotional support from a psychologist. | Activity and independence of children during classes. Showing initiative. |
| Lesson 4. Goal: developing self-control skills in the process of group interaction | ||
| Greeting Game 1. “Blinkers” Children are divided into pairs. The task is to look at each other intently for as long as possible without blinking. The winner chooses with whom he will continue the game. Game 2. “Mirror” The presenter portrays one of the animals. Group members guess. The presenters take turns changing. Game 3. “Everything is the other way around” The psychologist invites the children to split into pairs. Each pair is given cards that symbolically depict the movements. For example, hands up, right, left. Players must perform these movements as quickly as possible, but in reverse. The leader estimates the number of errors. Then the children change roles. | Children's liking for each other (pair choice) Children's ability to communicate constructively Development of self-control skills | Children's interest in the activity. Desires for group interaction. Adequate assessment of your failures. |
A diagnosis can only be made specialist - psychoneurologist. No teachers or social workers, no matter how qualified they are, can make a “sentence.” However, if you yourself feel that your child is lagging behind in development, and, even more so, if you have been advised to consult a specialist, this should be done immediately: the sooner treatment and correction begin, the easier it is to rid the child of this problem.
Researchers call the most striking sign of mental retardation immaturity of the emotional-volitional sphere.
In other words, it is very difficult for such a child to make a volitional effort on himself, to force himself to do something. And from here they inevitably appear attention disorders: its instability, decreased concentration, increased distractibility. Attention disorders may be accompanied by increased motor and speech activity.
Such a complex of deviations (attention deficit + increased motor and speech activity), not complicated by any other manifestations, is currently referred to as “attention deficit hyperactivity disorder” ().
Perception disturbance is expressed in the difficulty of constructing a holistic image. For example, it may be difficult for a child to recognize familiar objects from an unfamiliar perspective. This structuredness of perception is the cause of insufficient, limited knowledge about the world around us. Also speed of perception and orientation in space suffers .
If we talk about memory features in children with mental retardation, one pattern was found here: they remember visual (non-verbal) material much better than verbal material. In addition, it was found that after a course of special training in various memorization techniques, the performance of children with mental retardation improved even in comparison with normally developing children.
ZPR is often accompanied speech problems , related primarily to the pace of its development. In children with mental retardation there is delay in the development of all forms of thinking; it is detected primarily during solving problems of verbal and logical thinking. By the beginning of school, children with mental retardation do not fully master all the intellectual operations necessary to complete school assignments. (analysis, synthesis, generalization, comparison, abstraction).
It is very important to start implementing a correctional program as early as possible - then the child will have enough time to go to school prepared and not bear the “seal” of failure from the first grade. Medication support and corrective classes should begin as soon as the psychoneurologist has suggested a diagnosis; children with mental retardation or mental retardation have several combined disorders that depend on each other - so problems with self-control naturally lead to problems of attention, concentration, and these in turn lead to problems of general and intellectual development.
In our center, the problem of mental retardation and mental retardation is solved comprehensively by several specialists - a speech therapist, a speech therapist, a neuropsychologist, and a movement therapist.
State budgetary preschool educational institution
kindergarten No. 17 of a compensating type in the Kalininsky district
St. Petersburg
Summary of an open lesson for a speech pathologist teacher
using ICT
in the pre-school group.
Lexical topic:"Zimushka-winter"
Prepared by a speech pathologist teacher
GBDOU d/s No. 17 - Gudkova O.V.
Saint Petersburg,
February 2019
Target - consolidate knowledge about the signs of winter and teach them to apply them in practical and play activities.
Tasks:
Correctional educational:
1. Clarify and consolidate children’s knowledge about the signs of winter, consolidate the names of the winter months.
2. Strengthen spatial concepts (spatial orientation on a plane, understanding of prepositions).
3. Strengthen basic mathematical concepts (consolidate ideas about geometric shapes, consolidate knowledge of the number series from 1 to 10, ordinal counting up to 10, the ability to solve examples of addition and subtraction within 10).
Correctional and developmental:
1. Develop thinking (the ability to exclude an object from a series, explain your choice, the ability to solve riddles, explain their meaning),
2. Develop speech (work on compiling a coherent story based on supporting pictures, on the expressiveness of speech when telling poetry, on dialogical speech).
3. Develop visual memory, attention, perception (composing a whole from parts).
4. Develop general and fine motor skills (finger exercises, speech with movement).
Correctional and educational:
1. Creating a positive emotional background, goodwill.
2. Develop communication skills - the desire to complete tasks together and get results.
Materials : media equipment (interactive whiteboard, laptop, projector), envelope with snowflakes with tasks, cards for the game “Winter Sudoku”, cards for solving examples “Snowmen and Mittens”, game “Collect a Snowflake”, box “Magic Chest”.
Progress of the lesson:
1. Org. moment
Guys, this morning I received an unusual letter. Look how beautiful it is. Let's open it and read, who is it from?
"I am snow-white Winter,
And you all know me.
I am a garden and I have silvered the forest,
I went sledding down the hill,
She gave me a big Christmas tree.
It's time for me to leave,
I will part with you soon.
I want to test your knowledge and have prepared tasks..."
Guys, winter has prepared winter tasks for you on snowflakes. You will need to remember everything you know about winter. Be attentive and resourceful and you will succeed. And I will help you.
Are you ready to complete winter tasks?
2. Compiling a story about winter using reference pictures.
Snowflake No. 1:
Here's your first snowflake,
And she has a task.
Tell me, friends,
What kind of winter am I?
Slides 2-3 (pictures – seasons, winter months)
Guys, look at the board and tell me what time of year it was before winter? What time of year will it be after winter?
Winter has three brothers, three winter months. What are their names? (December January February).
What month is it now? (February).
Now remember what happens in winter? Name the winter signs from the pictures.
Slide 4
Children name the signs of winter based on reference pictures:
It's cold in winter. The sun shines, but does not warm. There is snow in the winter. A cold wind often blows, there are blizzards and blizzards. Rivers freeze and become covered with ice. The trees and bushes are bare. Birds are cold and hungry in winter. You need to make bird feeders and feed the birds. In winter, animals molt, bears and hedgehogs hibernate, and squirrels store food for the winter. In winter, people wear warm clothes: fur coats, hats, scarves, mittens, boots. In winter you can sled, ski, skate, make snowmen, play snowballs.
3. Guessing riddles.
Snowflake No. 2:
Guess you guys
My winter mysteries.
Guys, you need to guess the winter riddles, then the snowballs will melt and the answer pictures will appear.
Slide 5
Puzzles:
1.What kind of through stars?
On a coat and on a scarf.
All through, cut-out,
And if you take it, there is water in your hand (snowflakes)
2. He breathed on the window -
It instantly became covered with ice.
Even birch branches
Covered with frost... (frost)
3. No boards, no axes
The bridge across the river is ready.
Bridge like blue glass
Slippery, fun, bright! (ice)
4. Who sweeps and gets angry in winter,
Blowing, howling and spinning?
Making a white bed?
This is a snowy...(blizzard)
5. I live under the very roof,
It's scary to even look down.
I could live higher
If only there were roofs there. (Icicle)
Children solve riddles and explain their meaning. Guessing pictures appear on the slide.
4. Finger gymnastics (using kinesiological exercises)
Snowflake No. 3:
Tell me a poem about me,
And you will show the movements with your hands.
Guys, let's do finger exercises together and tell a poem about winter.
Winter has come, ( three palms touching each other)
Brought frost. (we massage the shoulders and forearms with our fingers)
Winter has come, (three palms touching each other)
Nose freezes. (use your palm to massage the tip of your nose)
Snow, (smooth movements with palms)
Snowdrifts, ( fists knock on knees alternately)
Ice. (palms shuffle across knees in different directions)
Everyone on the street - forward!(one hand on the knees with the palm, the other hand bent at the elbow-fist (change)Let's put on warm pants,(we run our palms over our legs)
A hat, a fur coat, felt boots. (We run our palms over the head, along the arms, stamp our feet)
Let's warm our hands in mittens (circular movements of the palms of one hand around the other palm)
And we'll tie scarves. (Place your palms on top of each other at the base of the neck)
Call it winter month!(palms tapping on knees)
December January February.(fist, rib, palm)
5. Game “Winter Sudoku”
Snowflake No. 4
You need to arrange the pictures,
Just... watch carefully,
So that they don't repeat themselves,
And then we all admire you.
Guys, you need to arrange the missing pictures so that they are not repeated in a row, either from left to right or from top to bottom.
Children complete the task. Then they take turns telling how the pictures were laid out.
6. Game “What’s extra?”
Snowflake #5:
Here's another snowflake -
Look at the pictures.
You tell me, friends,
What is unnecessary to remove here?
Slides 6-9
Images:
Snow, rain, icicles, snowman
A fox is hunting for a mouse, a bear with cubs, a hare in a white coat, a squirrel in a gray coat
Bullfinch, crow, tit, stork
Children make a snowman, sledding, skiing, a boy rides a bicycle
Children name the extra picture and explain their choice. The extra picture on the slide disappears.
7. Physical education lesson “Snowman” (speech with movement)
Snowflake No. 6
Now, quickly get up
Play an outdoor game.
I suggest moving around a little. Get into a circle. Let's build a snowman.
Come on, buddy, be brave, buddy,
Roll your snowball in the snow.
Children walk in a circle, one after another, pretending to roll a snowball in front of them.
It will turn into a snowball
They stop and “draw” a lump with both hands.
And the lump will become a snowman.
“Draw” a snowman from three circles of different sizes.
His smile is so bright
They show a smile on their face with their hands.
Two eyes, a hat, a nose, a broom.
They show their eyes, cover their head with their palm, show their nose, stand up straight, and hold an imaginary broom.
8. Game “Snowmen and Mittens”
Snowflake No. 7
Pick up mittens for the snowmen,
To do this, solve the examples rather.
Guys, let's pick out mittens for the snowmen. To do this, you need to solve examples on mittens and find the snowman with the answer number.
Children solve examples and tell the solution.
9. Game “What is where?”
Snowflake No. 8
Look at the pictures,
Tell me what is where.
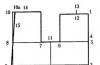
Slide 10
Guys, look carefully at the pictures and name what is in the upper right corner?
(“In the upper right corner there is a sled.”)
Right. What's in the lower left corner? (“There is a snowman in the lower left corner)
What's above the snowman? (Above the snowman are skis.)
What's under the sled? (There are snowballs under the sleds.)
What is between skis and sleds? (There are skates between them)
What's between a snowman and snowballs? (Between the snowman and the snowballs there is a hockey stick)
Slide 11
The pictures disappear.
And now, you need to remember where the pictures were. What was the top right corner? in the lower left corner? Etc.
Children name, pictures appear on the slide.
10. Game “Make a snowflake” (from geometric shapes)
Snowflake No. 9
Now take the figures
And collect snowflakes from them.
Guys, collect snowflakes from geometric shapes.
Children collect snowflakes according to the pattern. Then they name the shapes that make up the snowflake.
11. Summary of the lesson. Reflection.
Snowflake No. 10
You tried really hard today
We did so well.
I want to reward you
Perform magic for you.
Put my snowflakes in the chest
And say the magic words
"One two Three,
Turn snowflakes into a surprise!”
Slide 12 (picture depicting Winter)
The defectologist puts snowflakes in the chest. He pronounces magic words together with the children.
Opens the chest and gives prizes to the children.
-
Did you like the surprise of winter?
Well done. Today you were attentive, resourceful and showed that you know a lot about the winter season.
Slide captions:
Lesson using ICT with children with disabilities and mental retardation (preparatory group). “Zimushka - winter” Prepared by Gudkova O.V. teacher-defectologist GBDOU kindergarten No. 17 Kalininsky district of St. Petersburg State budgetary preschool educational institution kindergarten No. 17 of a compensating type Kalininsky district of St. Petersburg